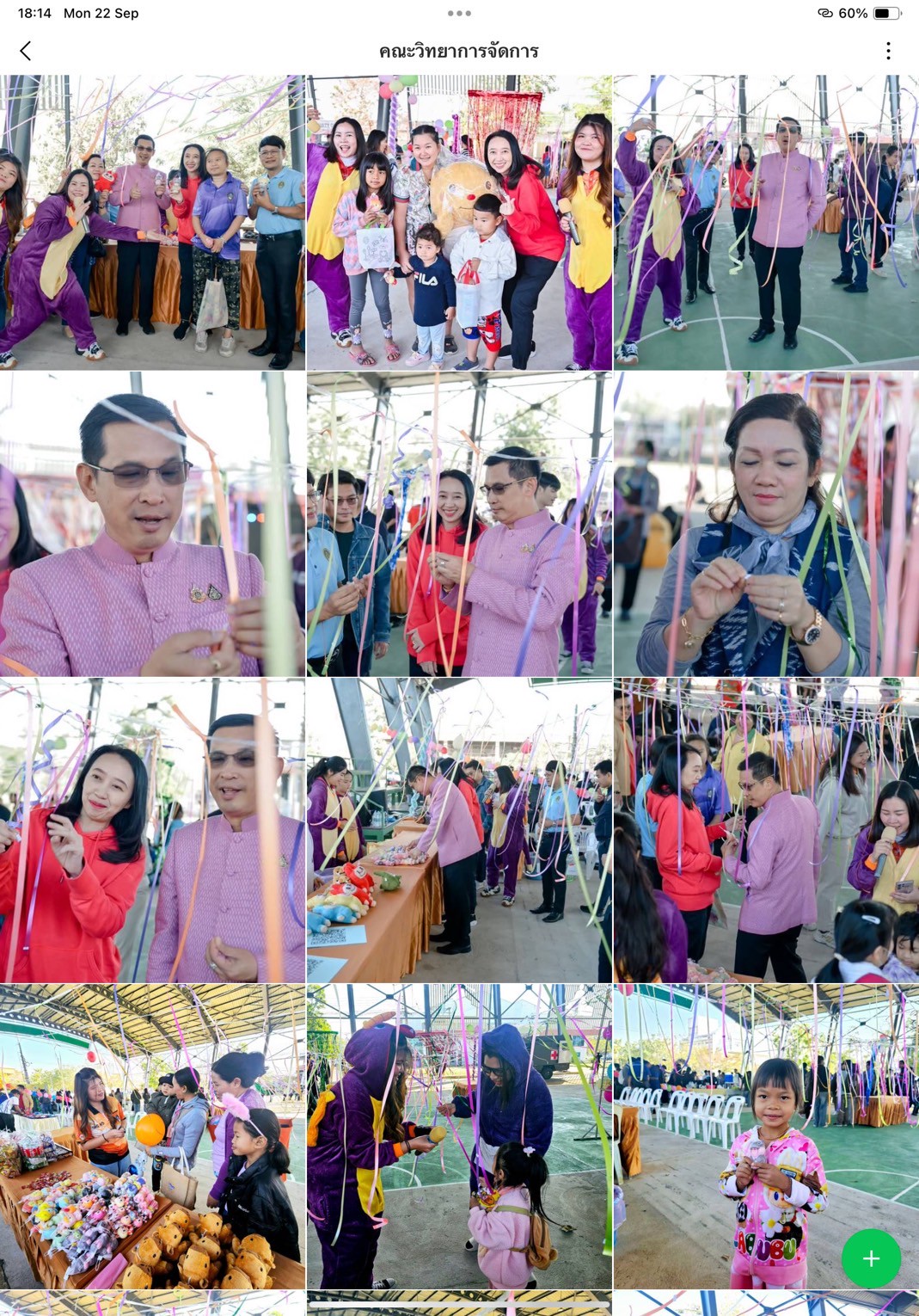
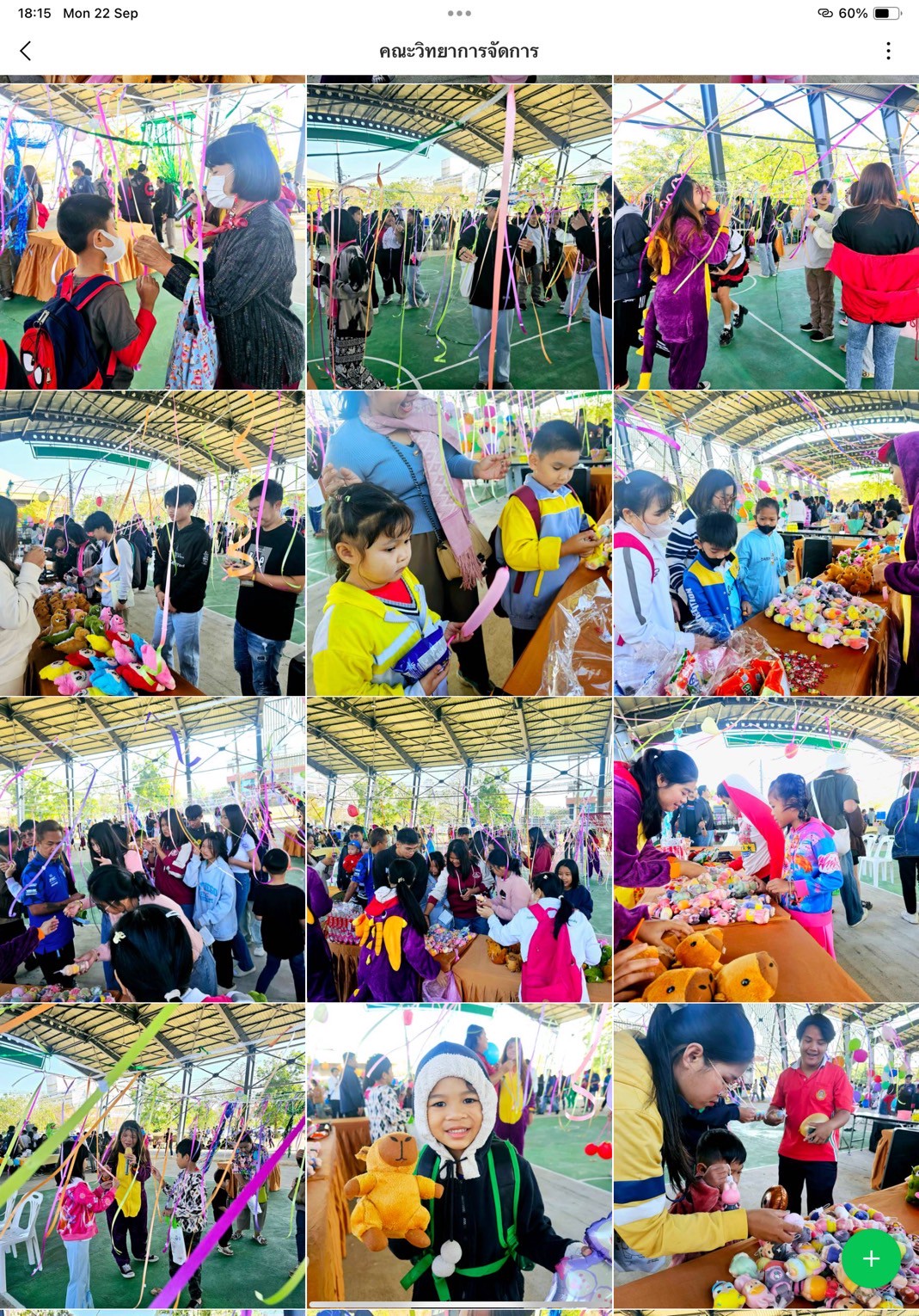
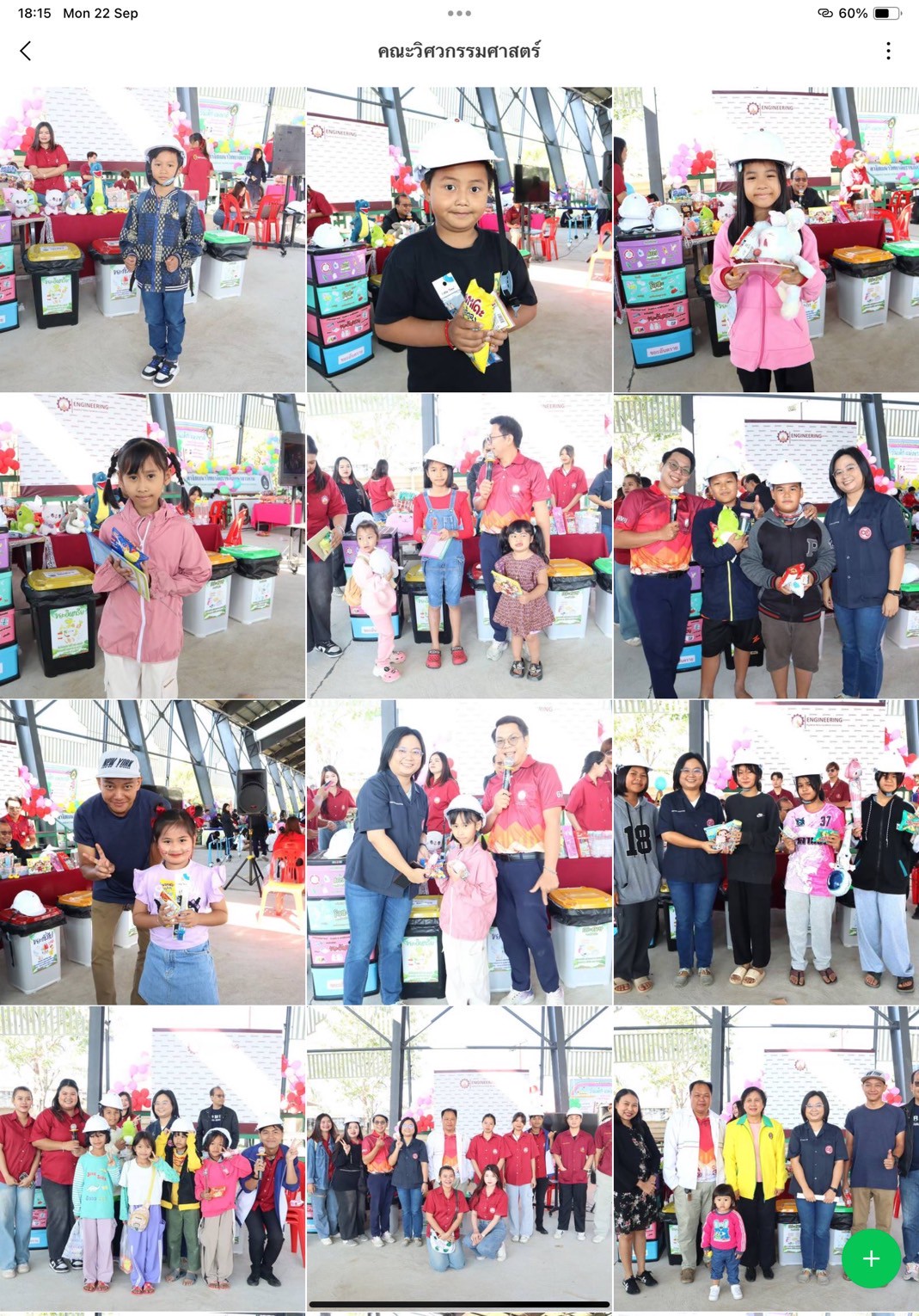
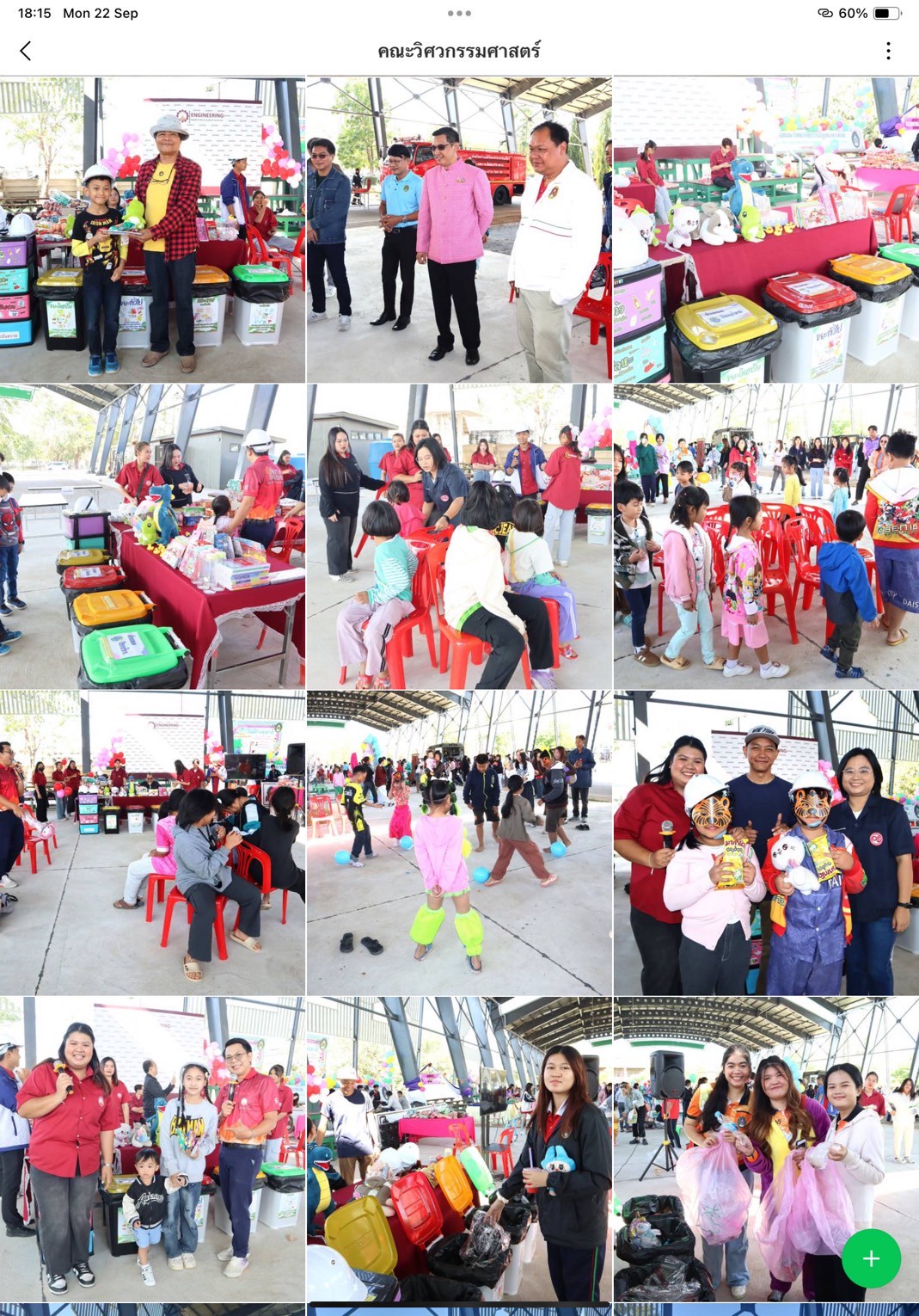
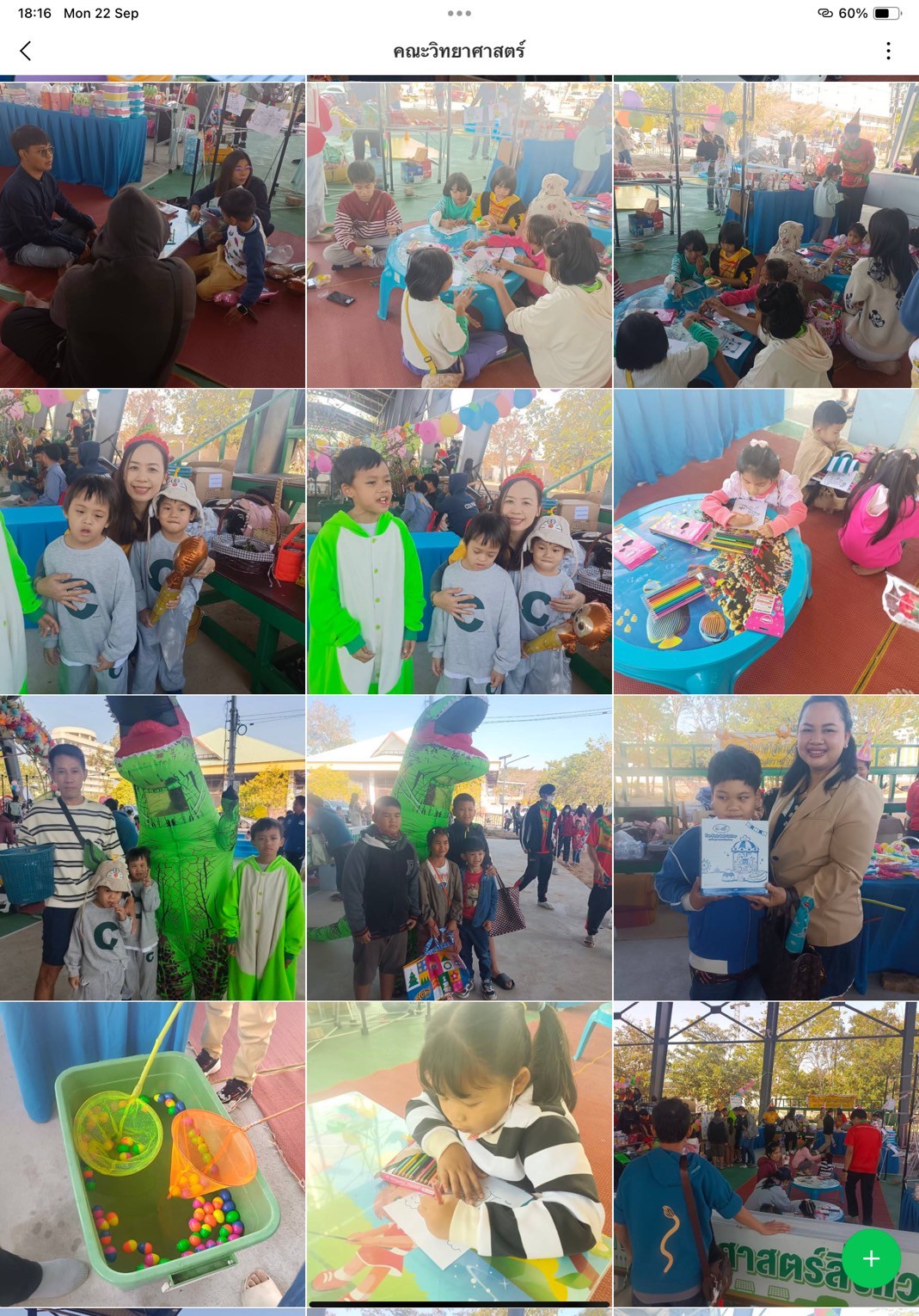
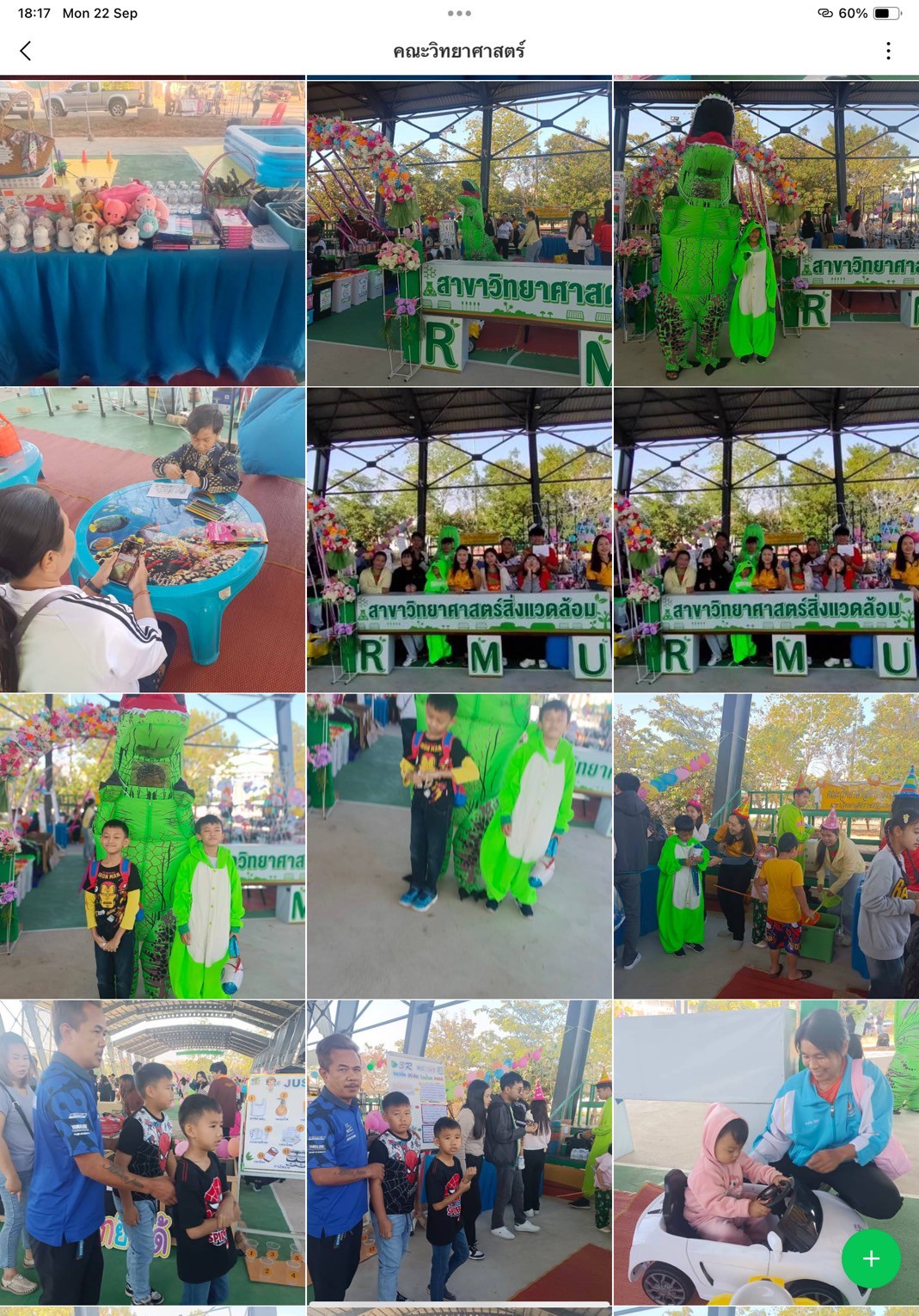
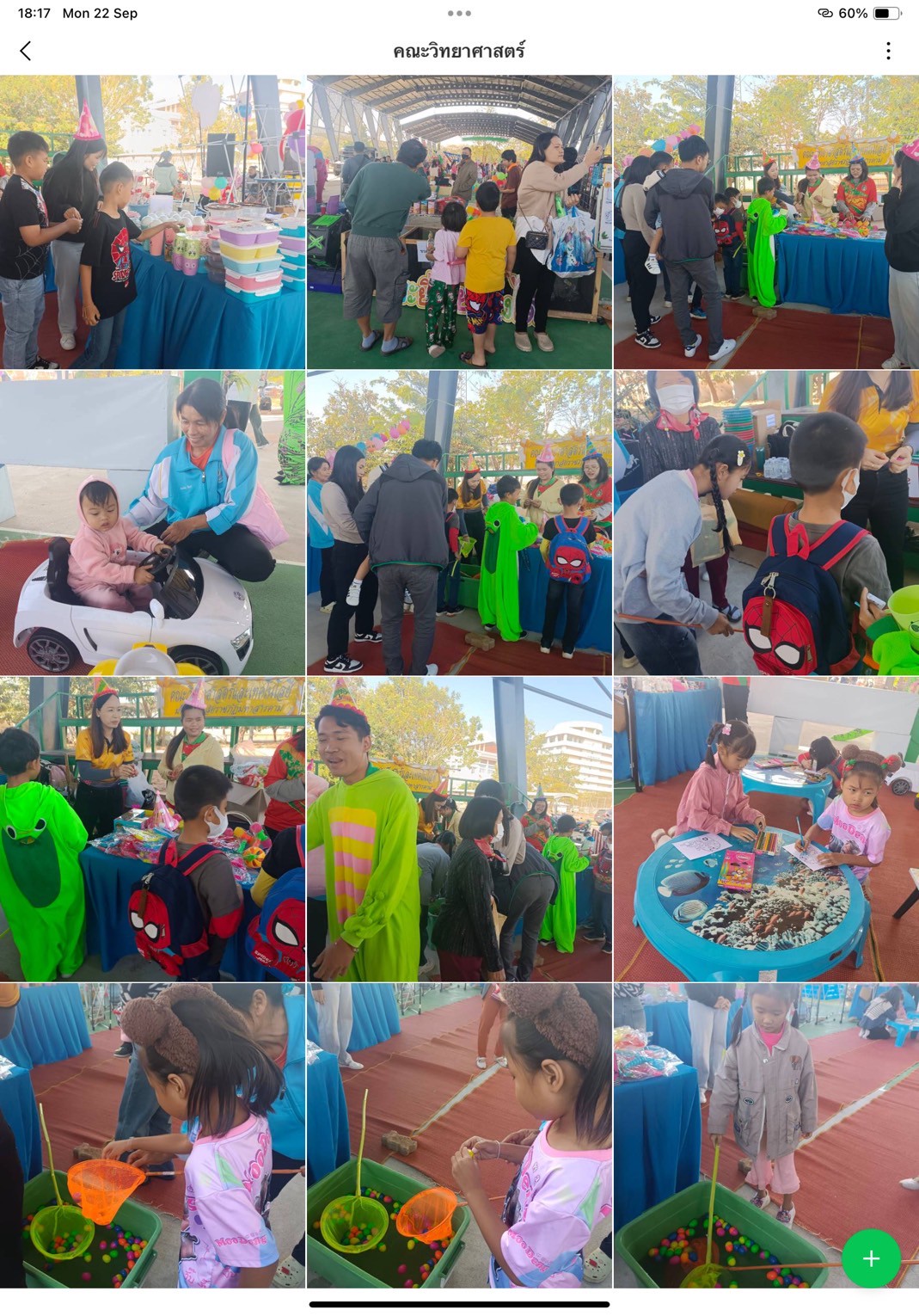
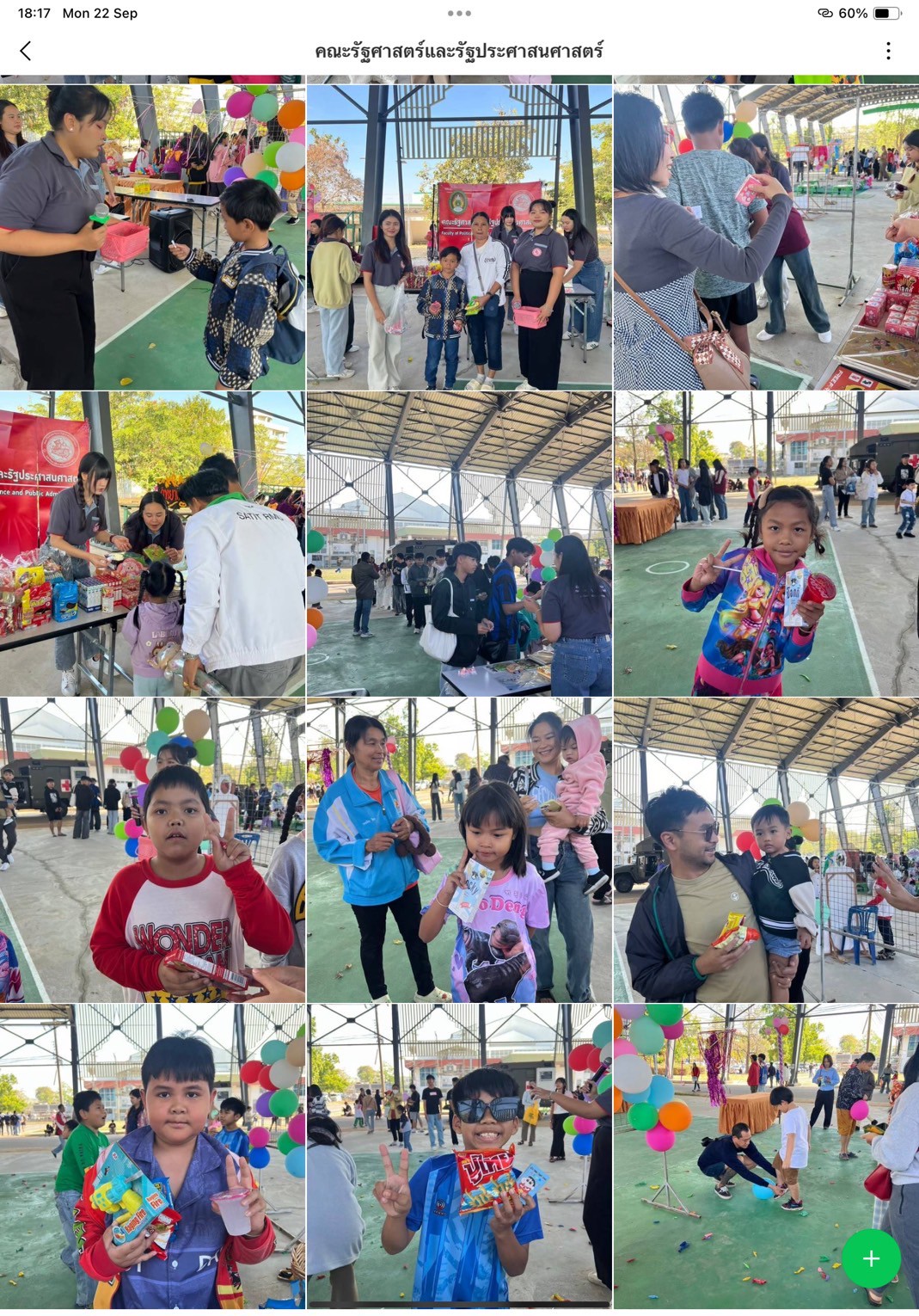
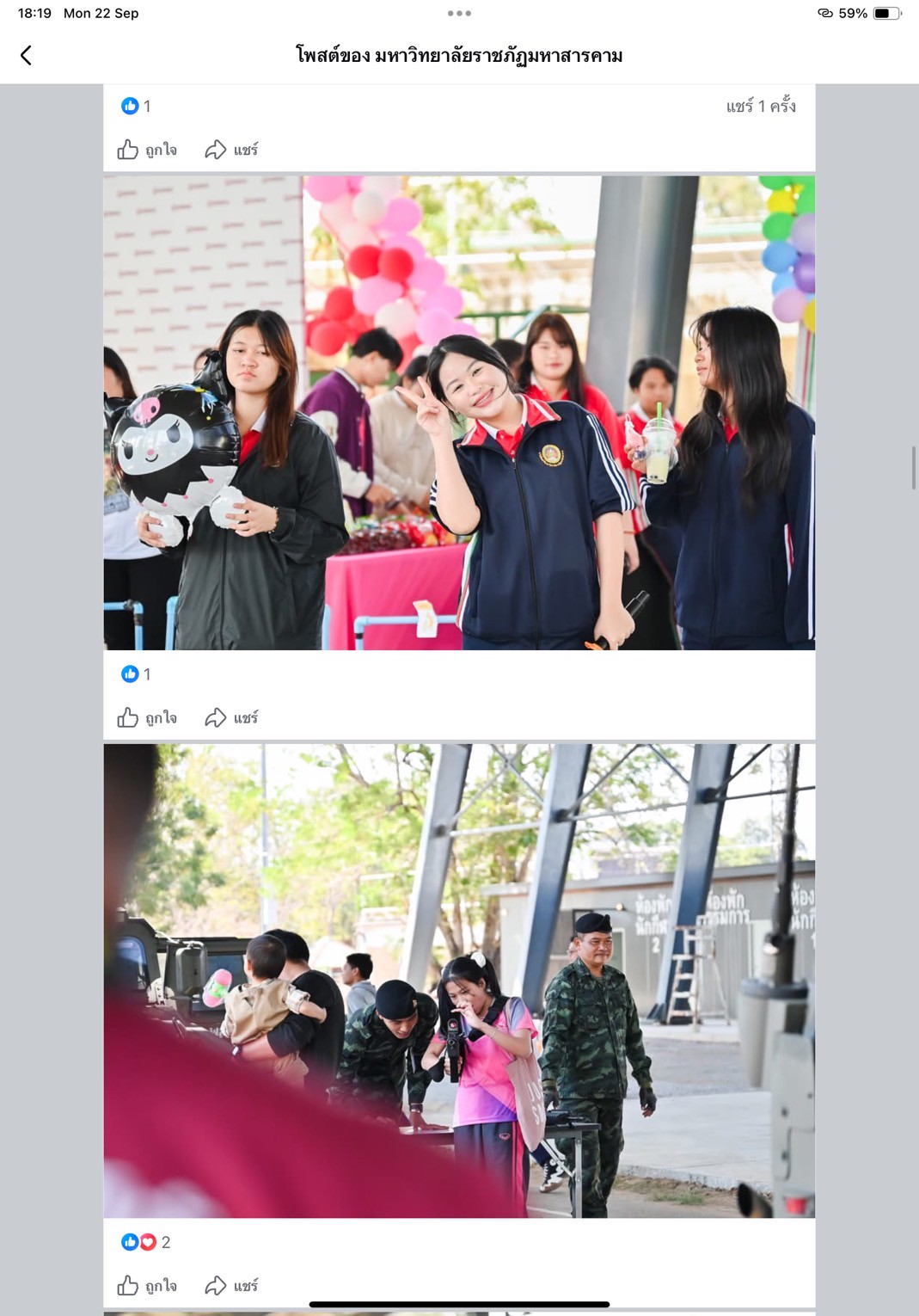
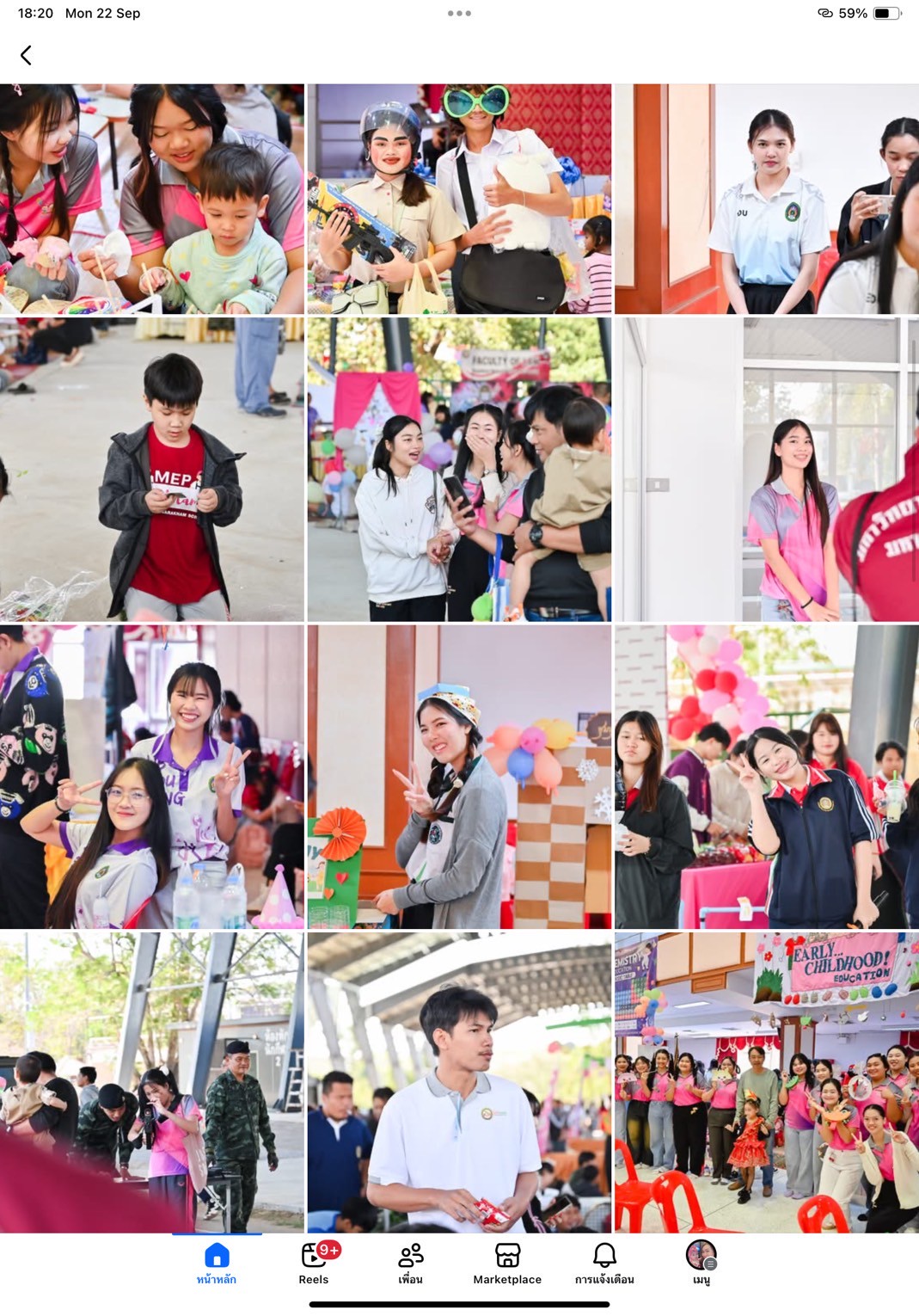
Thailand New Gen Loves the Earth
ผู้รับผิดชอบ ให้ข้อมูล : ผศ.ดร.พันธิวา แก้วมาตย์
SDG ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
เป้าหมายย่อย เป้าหมายย่อยความสอดคล้องกับยุทธศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัย : พันธกิจสัมพันธ์เพื่อการพัฒนาท้องถิ่นอย่างสร้างสรรค
แหล่งงบประมาณ : งบประมาณแผ่นดิน
กลุ่มเป้าหมาย : นักศึกษา
Project Implementation Area : มหาวิทยาลัยราภัฏมหาสารคาม ตำบล Talat อำเภอ Mueang Maha Sarakham จังหวัด Maha Sarakham 44000
Project Duration: January 9, 2025 – January 11, 2025
Objectives :
1. To promote environmental awareness and responsibility among Thai children and youth by fostering environmental consciousness through activities that encourage sustainable participation in environmental conservation.
2. To motivate young people to engage actively in environmental protection, recognize the importance of safeguarding the planet, and apply these practices in their daily lives.
3. To develop the capacity of participating children and youth to think critically and creatively about resource management, particularly through reusing materials and reducing excessive consumption.
Activities :
- Activity 1: Environmental Awareness for the New Generation: This activity aims to promote understanding and participation in environmental conservation among youth through interactive learning, workshops, and lectures on environmental crises such as global warming, waste management, food waste, natural disasters, biodiversity loss, and natural resource preservation. The approach emphasizes creative and engaging methods to inspire youth toward sustainable behavior change.
- Activity 2: Value-Added Crafting from Reused Materials — “From Waste to Worth: Creativity for the Environment”: Participants learned to repurpose discarded materials into valuable products, promoting recycling (Recycle) and resource efficiency. The activity encouraged creativity, imagination, and out-of-the-box thinking through the creation of handmade items from waste, while also introducing potential income-generating skills and sustainable craft development.
Activity 3: Inspiring Thai Youth to Love the Earth through Practice-Based Learning: Designed to instill positive environmental behavior from an early age, this activity combined fun and hands-on learning through everyday eco-friendly practices such as waste separation, tree planting, creating natural-material flowerpots, demonstrating energy conservation, crafting toys from recycled materials, and performing “Little Eco Hero” shows.
Number of project participants: 1500 people
Project Budget: 350,000 Baht
Results :
Economic Dimension:
- Encouraged the development of ideas and approaches for supplementary occupations that can generate additional income.
- Promoted learning among children and youth about waste separation and recycling as means to earn extra income from selling recyclable materials and reusing items. This initiative helps reduce the volume of waste requiring disposal, thereby lowering community waste management costs.
Social Dimension:
- Fosters a collective sense of environmental responsibility within the community by cultivating environmentally conscious and responsible children and youth who will grow into socially responsible adults.
- Encourages participants to recognize their personal role and importance in environmental conservation, enabling them to apply environmentally friendly practices in daily life and participate actively in community-based environmental initiatives.
Educational Dimension:
- Integrates knowledge acquisition with hands-on experience, thereby enhancing learning development among participating children and youth.
- Instills a sense of responsibility from an early age by teaching children sustainable resource management practices such as reducing plastic use, reusing materials, and recycling.
Environmental Dimension:
- The project activities emphasized the theme “Love the Earth, Protect the Environment,” fostering awareness and understanding among participants and empowering them to take part in long-term, sustainable environmental stewardship.
Results society :
- Benefits to Participants: Children and youth gained knowledge about pressing environmental issues—such as global warming, waste generation, and natural resource depletion—through engaging, practice-based learning. The activities promoted environmental understanding and practical behavior change (e.g., waste sorting, energy saving, creative reuse), while developing critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and teamwork skills that contribute to long-term youth empowerment.
- Benefits to the organizer/University: The project reflected Rajabhat Maha Sarakham University’s proactive commitment to its vision of becoming “a high-quality university for strong and sustainable local development.” It enhanced the institution’s image as a leader in environmental and human development, fostered academic collaboration, and strengthened networks with local communities—laying the foundation for future research, academic services, and genuine local development.
- Benefits to the Community/Society:The project nurtured environmentally responsible citizens who influence positive change in families and communities. Youth participants served as catalysts for behavioral transformation in waste reduction, resource conservation, and urban greening. The project also showcased effective collaboration between educational institutions, youth, and communities in addressing environmental challenges sustainably.
Participation :
Students Participtation
1. Course: Ecology and Conservation Biology (206702105)
The project activities—such as tree planting, waste separation, and recycling crafts—were integrated into lessons on ecological relationships and biodiversity conservation.
Teaching Applications:
- Implement Project-Based Learning (PBL) to conduct small-scale ecological surveys or plant species studies.
- Facilitate field data collection and analysis exercises related to environmental conditions.
- Conduct discussions or seminars on the societal roles of conservation.
2. Course: Global Warming and Disasters (826624013)
Lectures and workshops from the project were incorporated into classroom content on global warming, pollution, and climate change., integrating with recycling, energy saving with GHV emission, using Little Heroes activity as as easy learning medium.
Teaching Applications:
- Assign students to create reports or infographics on “Everyday Actions to Reduce Global Warming.”
2. Use simulation and case-study discussions linking project findings to academic theories.
3. Employ the “Little Eco Hero” performance as an interactive learning tool to simplify environmental concepts. Faculty Participation: Each faculty organized thematic activities promoting creativity and environmental awareness:
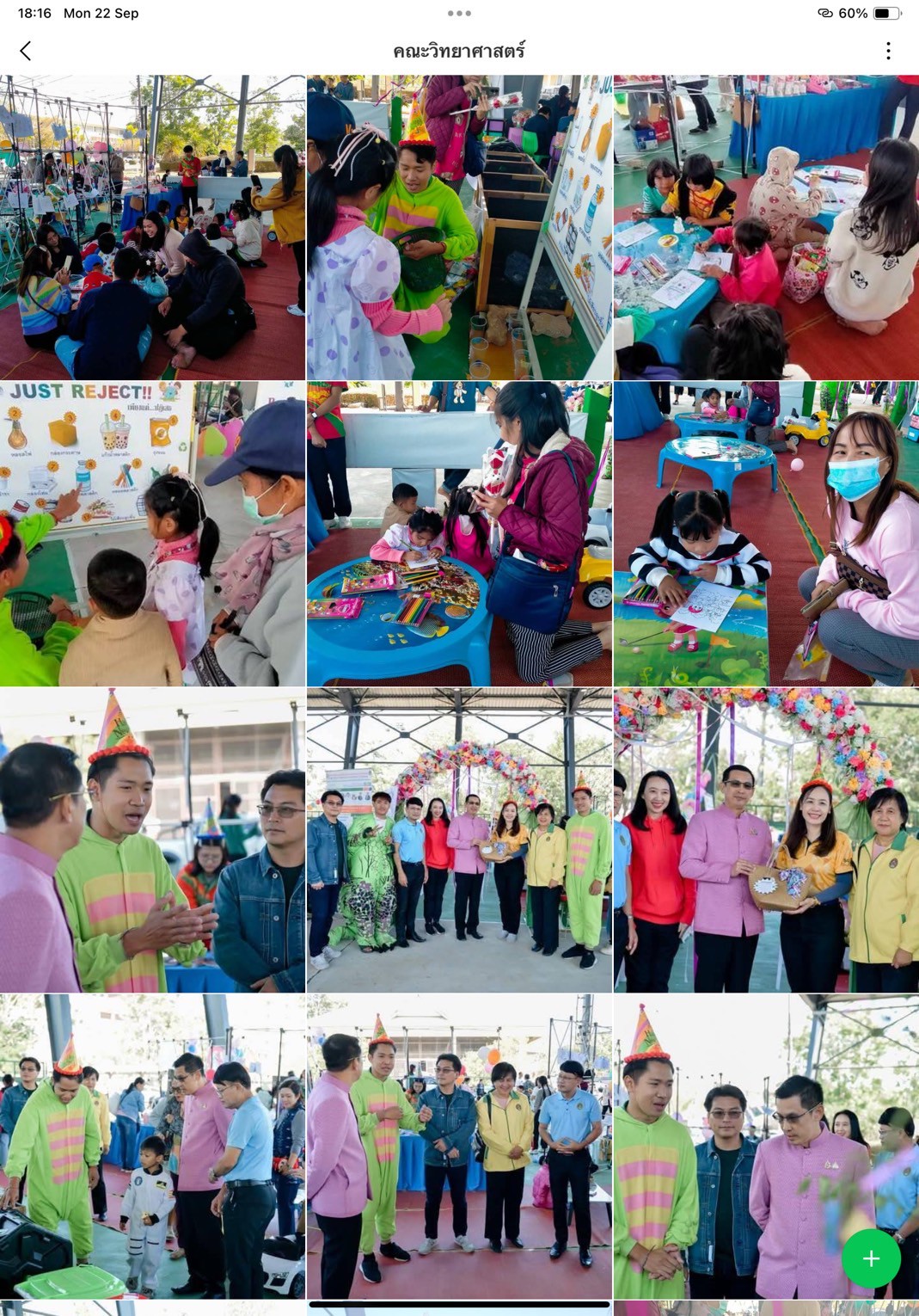
- Faculty of Science and Technology: ZERO WASTE KIDS – Fun and Green for a Cooler Planet
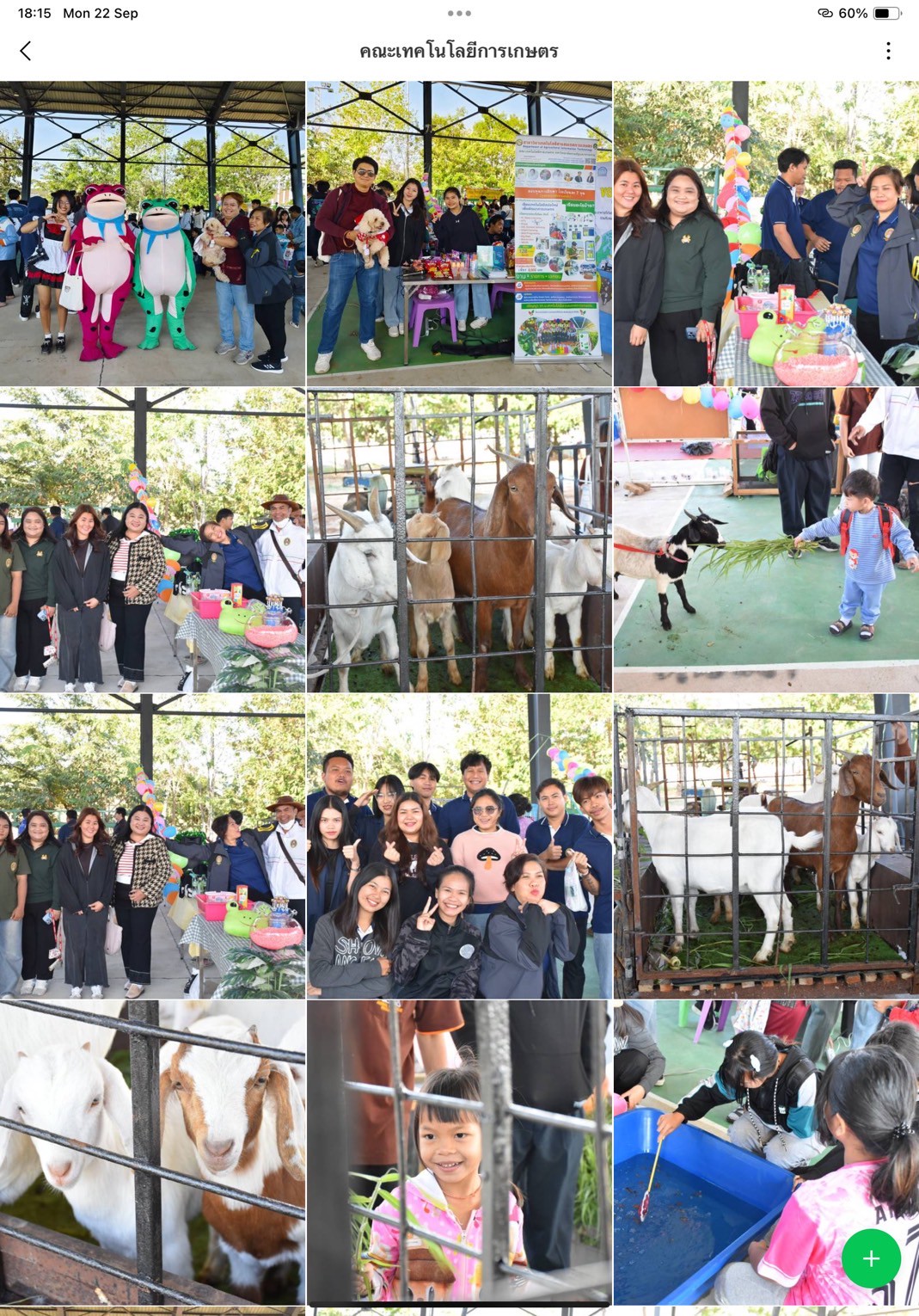
- Faculty of Agricultural Technology: Farmland Animal Park
- Faculty of Management Science: Star Hunt Eco Game
- Faculty of Information Technology: IT ROV E-SPORT
- Faculty of Political Science and Public Administration: Fun Box Challenge
- Faculty of Education: EDU Kids – Learning Green, Growing Future
- Faculty of Law: “Law Rak (Protects) the Earth”
- Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences: Creative Eco-Bag Art
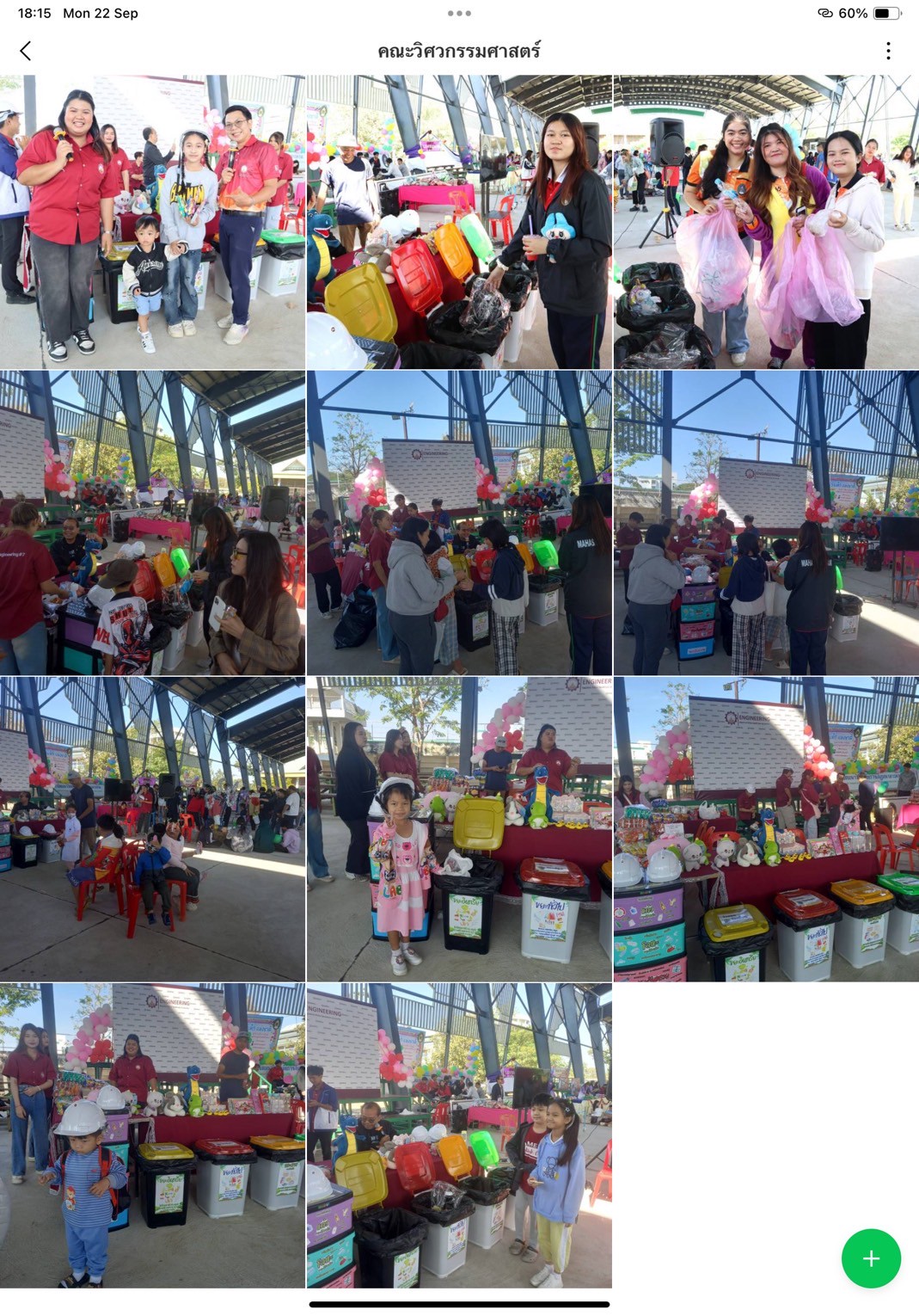
- Faculty of Engineering: “Junior Eco Engineers”
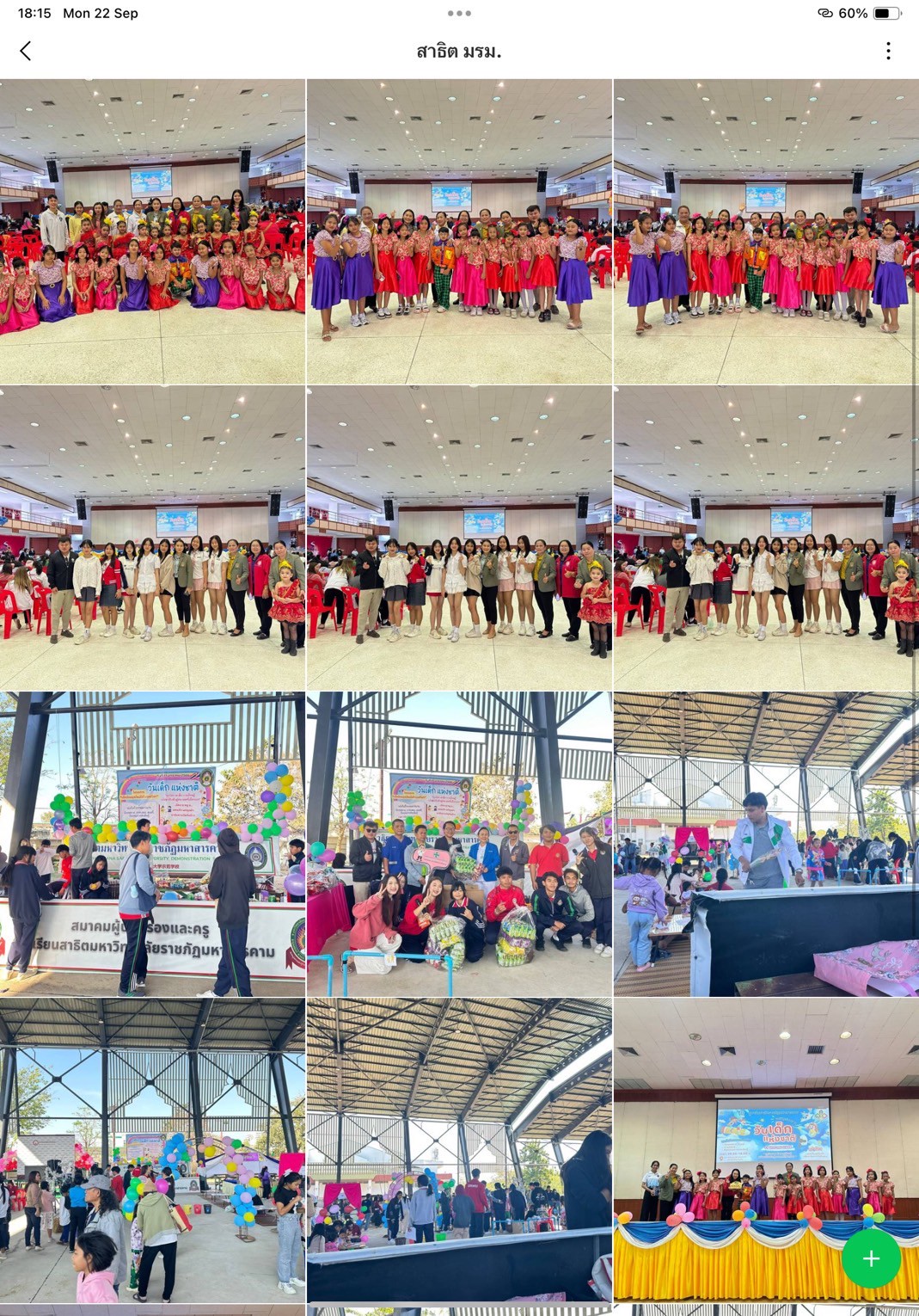
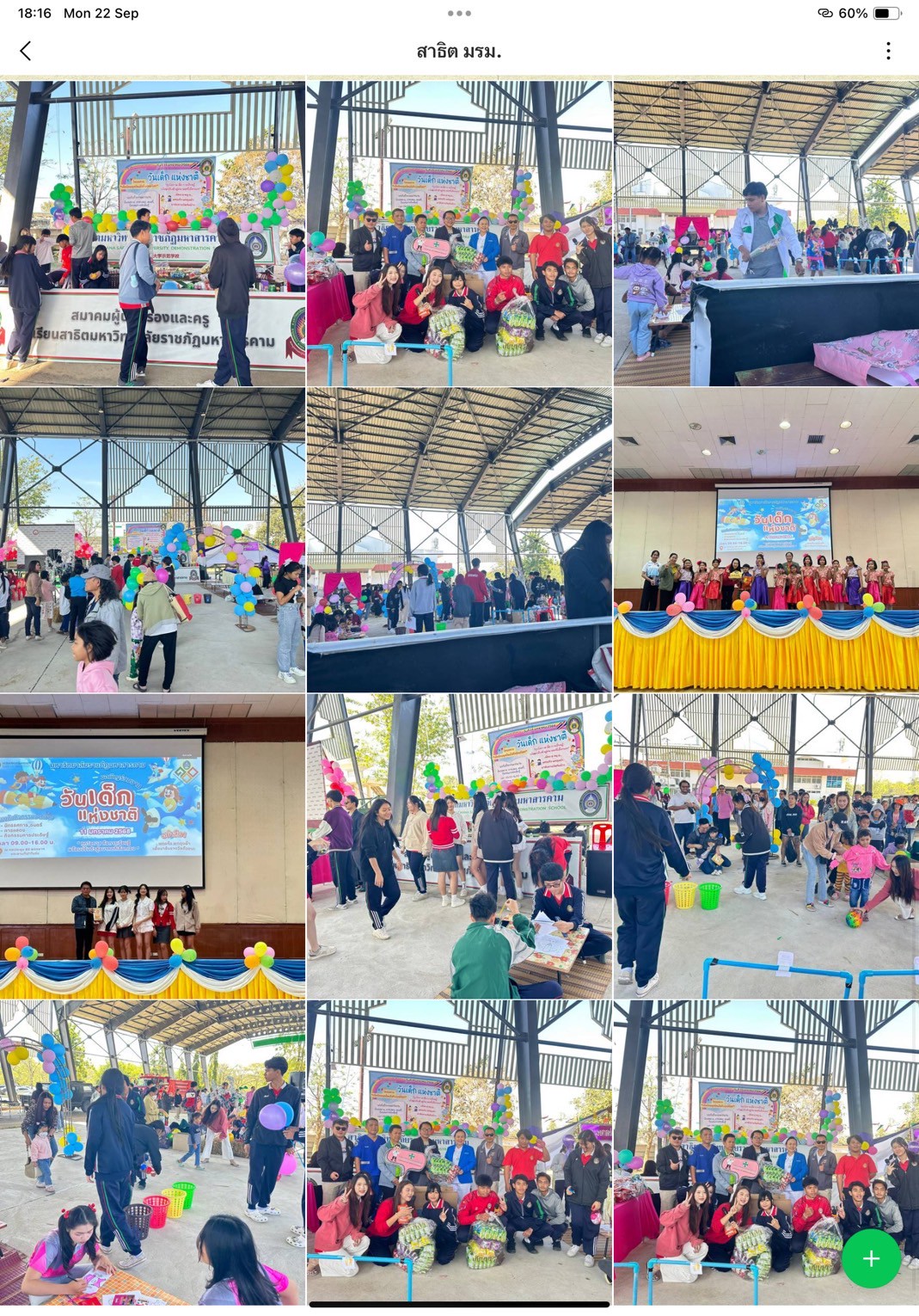
- Demonstration School: TikToker Kids, Eco Showcase, and Cover Dance Hype Boy–Nawjens One Dream
These on-site activities provided interactive learning platforms, combining fun, creativity, and environmental education, with key learning outcomes:
1. Inspiration and Role Modeling — Youth participants were inspired by peers performing “Little Eco Hero” shows, fostering peer-to-peer environmental learning.
2. Creative and Practical Ideas — Demonstrations on crafting from recycled materials sparked innovative ideas applicable at home or school.
3. Enjoyable Learning — Environmental quizzes and games made knowledge acquisition engaging and memorable.
4. Positive Environmental Attitude — The playful, interactive format fostered lasting positive attitudes toward sustainability.
5. Network Building — Participants developed a sense of belonging to a growing network of eco-conscious youth.
Project continuity :
New project
Problems obstacles :
- Tight project timeline led to limited preparation time.
- Difficulties in follow-up and project evaluation, as the Faculty of Science and Technology managed the budget while multiple Education faculty programs executed the activities.
Improvement :
Time Management
- Develop an annual event plan (e.g., align with National Children’s Day) and include it in university or faculty action plans.
- Establish a permanent working committee comprising representatives from all relevant faculties for more efficient coordination.
- Implement Project-Based Management with a clear operational timeline and defined responsibilities.
- Assign clear accountability for each sub-activity with measurable indicators.
Suggestions :
Operational Management
- Include the project in the annual operational plans of faculties and the university.
Finance Management - Align financial procedures with actual implementing units, allowing faculties to manage disbursements directly.
- จัดทำแบบฟอร์มและขั้นตอนเบิกจ่ายกลาง เพื่อให้ทุกคณะใช้รูปแบบเดียวกัน ลดความซ้ำซ้อนและความล่าช้า